COLOR SHAPER
COLOR GRADING TOOL
INTRODUCTION
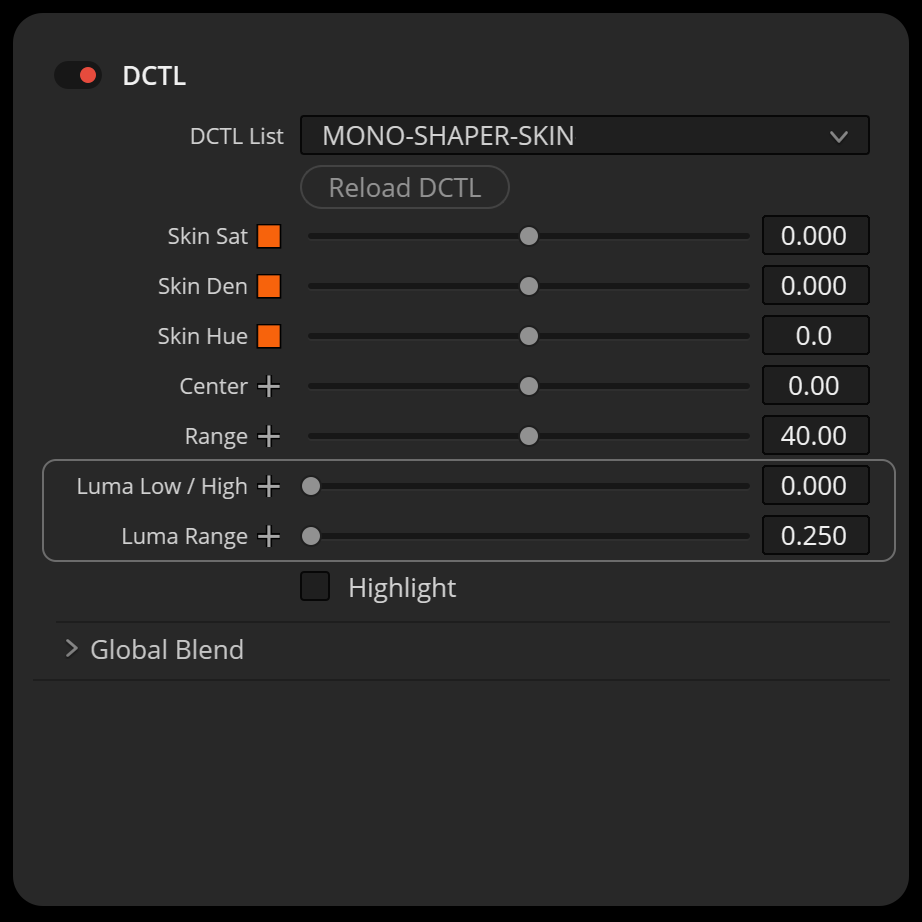
These DCTLs enable you to precisely select and modify a specific hue range, adjusting its saturation, density, or hue. Uniquely, these DCTLs also allow you to choose a luminance range within the selected hue, ensuring that adjustments affect only the shadows, midtones, or highlights. This targeted approach enhances precision in color grading, providing optimal control over the visual outcome.
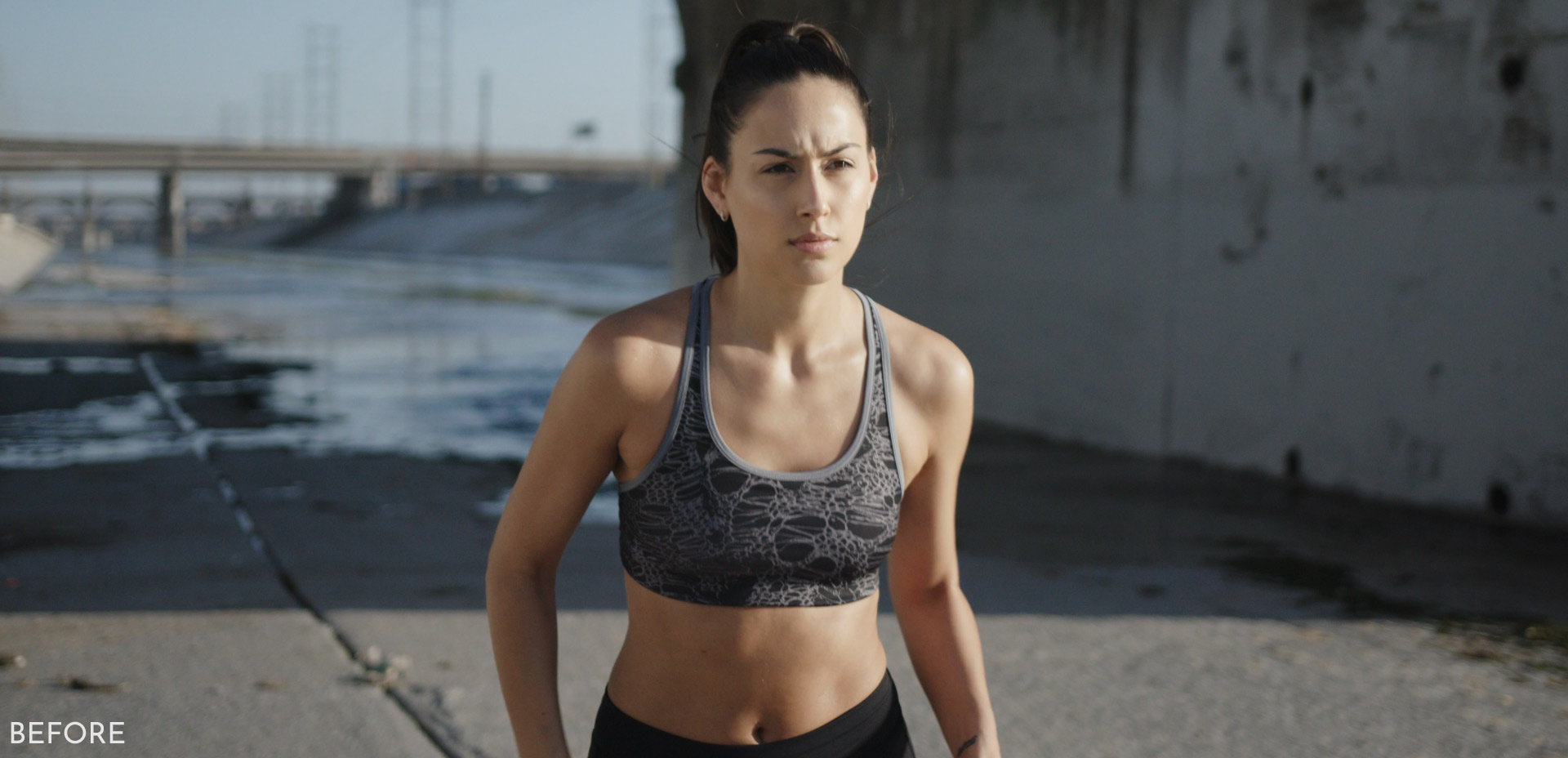
In this example, I applied more density and saturation to the shadow regions of her skin.
In this example, I brightened and added saturation to the highlight regions of his skin.
GUIDELINES
FOR HUE SELECTION
- Move the ‘Range’ slider to the left to set it to the minimum value of 15.00.
- Adjust the “Center” slider to pinpoint the desired hue, ensuring it is distinctly highlighted in the image.
- Increase the ‘Range’ slider back to around 40.00 degrees or more for a smooth rolloff between adjacent hues.
This image illustrates the flexibility of adjusting the ‘Center’ for ‘Cyan’. By using the ‘Center’ slider, you can extend the hue adjustments beyond pure cyan, reaching into hues that blend towards blue or green.

GUIDELINES
FOR LUMA SELECTION
- Begin by moving the ‘Luma Low/High’ and ‘Luma Range’ sliders to the leftmost position.
- Gradually increase the ‘Luma Low/High’ slider to selectively adjust the shadow or highlight regions as needed.
- Enhance the transition between dark and bright areas by slowly increasing the ‘Luma Range’ to achieve a smooth rolloff.
This image demonstrates the versatility of adjusting the ‘Luma Low / High’ values for ‘Cyan’. By using the ‘Luma Low / High’ slider, you can precisely select the shadow, midtone, and highlight regions of an image.

FAQ
What is the difference between the “Color Shift” DCTL pack and this tool?
The Color Shift DCTL pack is engineered for global color adjustments across multiple hues, making it ideal for efficiently developing a cohesive and comprehensive global look. It allows users to adjust six or seven hues within a single DCTL, enabling broad color changes and ensuring smooth transitions to neighboring hues and varying luminance values. Equipped with features like the Saturation Range and Deep Slider, Color Shift facilitates quick global modifications, making it well-suited for tasks such as global look development.
In contrast, Color Shaper is crafted for precise, targeted color adjustments focused on individual hues. Unlike Color Shift, Color Shaper adjusts one hue per DCTL, allowing for meticulous modifications that address specific color issues within a scene. Its adjustment controls include Center, Hue Range, Luminance, and Luma Range, which provide detailed manipulation of specific color parameters. These controls enable users to fine-tune the central hue, define the range of hues affected, and adjust brightness and luminance distribution with high precision. Additionally, Color Shaper serves as an alternative to DaVinci Resolve’s Qualifier tool, offering similar functionalities for selecting and refining specific color ranges but with enhanced precision and control.
In summary, Color Shift is optimized for broad, global color grading tasks, enabling efficient adjustments across multiple hues and facilitating consistent color grading across large projects. Conversely, Color Shaper is tailored for detailed, scene-specific color corrections, providing precise control over individual hues to address specific color-related issues. Together, these tools offer a versatile and comprehensive solution for colorists, allowing for both extensive color harmony and meticulous color accuracy based on project requirements.
What is the difference between this tool and the “Qualifier”?
Color Shaper fundamentally differs from mask-based methods like the Qualifier. While the Qualifier isolates specific color ranges for adjustment based on hue, saturation, and luminance values, it relies heavily on precise masking. Achieving seamless results with the Qualifier requires meticulous refinement of mask edges; without proper blurring, blending, smoothing, or softening, adjustments can appear harsh and unnatural, disrupting the overall quality of the scene.
Instead of relying on rigid masks, Color Shaper uses curve functions for the selection process. This approach allows the intensity of the effect to gradually decrease as it moves away from the center of the specified range. The result is a natural smoothness that avoids the harsh edges commonly associated with qualifiers, creating more seamless transitions between affected and unaffected areas. This method not only enhances the visual integrity of the scene but also simplifies the color grading workflow by reducing the need for extensive edge refinement.
This image provides a detailed view of the interface for the HSL Qualifier in DaVinci Resolve, highlighting the complexity and precision required to create a clean mask for color correction.
VIDEO
FREE DEMO VERSION
ko-fi.com / 2 MB
This version includes a watermark, displayed as a grid
of black plus signs on the image. The demo version is perfect
for users who want to explore the software’s features
and functionalities before making a purchase.
INSTALL GUIDELINES
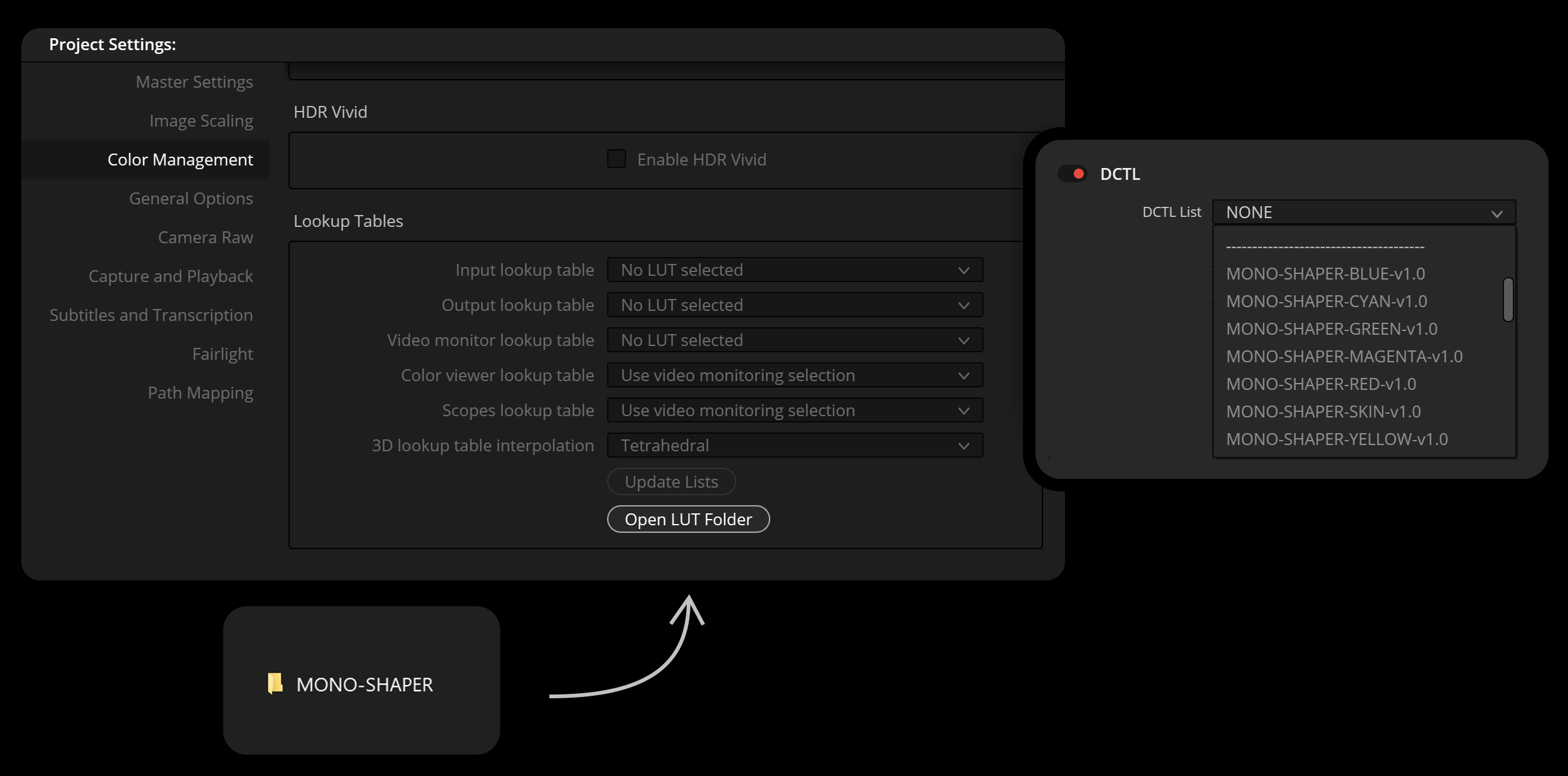
- Open the “Project Settings.”
- Go to “Color Management” and choose “Open LUT Folder.”
- Drag and drop the folders with the DCTL files into this directory.
- Restart DaVinci Resolve to apply the changes.
NODE TREE GUIDELINES
& COLOR SPACE
If you are using multiple ‘SHAPER’ DCTLs, I recommend using parallel nodes for optimal results.
COLOR SPACE:
This tool is designed to work best in large color spaces.
Such as DWG or LogC3.